Tahoe Workflow
Introduction
Tahoe is the Metal network's test network. You can use it to test your dapp or smart contract after you've developed it locally. (You can use Metal Network Runner to test things locally.) Tahoe is typically on the same version as the Metal Mainnet, but sometimes it is running an unreleased version of MetalGo. In general, you can expect Tahoe's behavior to be about the same as Metal Mainnet. Tools such as a explorers and wallets should work with the Metal Testnet.
In this tutorial, we’ll go through an example Tahoe workflow to show how it can be used. We'll do the following:
- Set up Tahoe network on MetaMask (optional)
- Generate a 24 word english mnemonic via MetalJS
- Derive external C-Chain addresses via MetalJS
- Get METAL from the Tahoe faucet
- Send METAL via ethersJS
- Examine the resulting transaction on the Metal Trace Explorer
- Use a private key derived from a mnemonic to sign into the web wallet
Set up Tahoe Network on MetaMask (optional)
- Network Name: Metal Tahoe C-Chain
- New RPC URL: https://tahoe.metalblockchain.org/ext/bc/C/rpc
- ChainID:
381932 - Symbol:
METAL - Explorer: https://tahoe.metalscan.io/
Generate a Mnemonic
To begin, we'll create a mnemonic phrase with MetalJS. Mnemonics enable us to encode strong security into a human-readable phrase. MetalJS supports 10 languages including English, Japanese, Spanish, Italian, French, Korean, Czech, Portuguese, Chinese Simplified and Chinese Traditional.
First, generate a 24 word english BIP39-compliant mnemonic via MetalJS.
import { Mnemonic } from "metal"
const mnemonic: Mnemonic = Mnemonic.getInstance()
const strength: number = 256
const wordlist = mnemonic.getWordlists("english") as string[]
const m: string = mnemonic.generateMnemonic(strength, randomBytes, wordlist)
console.log(m)
// "chimney asset heavy ecology accuse window gold weekend annual oil emerge alley retreat rabbit seed advance define off amused board quick wealth peasant disorder"
Derive Addresses
After generating a mnemonic we can use MetalJS to derive BIP32-compliant hierarchical deterministic (HD) Keypairs.
import HDNode from "metal/dist/utils/hdnode"
import { Avalanche, Mnemonic, Buffer } from "metal"
import { EVMAPI, KeyChain } from "metal/dist/apis/evm"
import { ethers } from "ethers"
const ip: string = "tahoe.metalblockchain.org"
const port: number = 443
const protocol: string = "https"
const networkID: number = 5
const avalanche: Metal = new Metal(ip, port, protocol, networkID)
const cchain: EVMAPI = metal.CChain()
const mnemonic: Mnemonic = Mnemonic.getInstance()
const m: string =
"chimney asset heavy ecology accuse window gold weekend annual oil emerge alley retreat rabbit seed advance define off amused board quick wealth peasant disorder"
const seed: Buffer = mnemonic.mnemonicToSeedSync(m)
const hdnode: HDNode = new HDNode(seed)
const keyChain: KeyChain = cchain.newKeyChain()
const cAddresses: string[] = []
for (let i: number = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
const child: HDNode = hdnode.derive(`m/44'/60'/0'/0/${i}`)
keyChain.importKey(child.privateKey)
const cchainAddress = ethers.utils.computeAddress(child.privateKey)
cAddresses.push(cchainAddress)
}
console.log(cAddresses)
// [
// '0x2d1d87fF3Ea2ba6E0576bCA4310fC057972F2559',
// '0x25d83F090D842c1b4645c1EFA46B15093d4CaC7C',
// '0xa14dFb7d8593c44a47A07298eCEA774557036ff3'
// ]
Generate Private Keys from a Mnemonic
As long as you have the mnemonic phrase, you can re-generate your private keys and the addresses they control.
For example, if you want to generate the private keys for the first 3 address in the C Chain keychain:
- 0x2d1d87fF3Ea2ba6E0576bCA4310fC057972F2559
- 0x25d83F090D842c1b4645c1EFA46B15093d4CaC7C
- 0xa14dFb7d8593c44a47A07298eCEA774557036ff3
you might update the example script above to the following:
const cAddresses: string[] = []
const privateKeys: string[] = []
for (let i: number = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
// Deriving the _i_th external BIP44 C-Chain address
const child: HDNode = hdnode.derive(`m/44'/60'/0'/0/${i}`)
keyChain.importKey(child.privateKey)
// Converting the BIP44 addresses to hexadecimal addresses
const cchainAddress = ethers.utils.computeAddress(child.privateKey)
privateKeys.push(child.privateKey.toString("hex"))
cAddresses.push(cchainAddress)
}
console.log({ cAddresses, privateKeys })
// {
// cAddresses: [
// '0x2d1d87fF3Ea2ba6E0576bCA4310fC057972F2559',
// '0x25d83F090D842c1b4645c1EFA46B15093d4CaC7C',
// '0xa14dFb7d8593c44a47A07298eCEA774557036ff3'
// ],
// privateKeys: [
// 'cd30aef1af167238c627593537e162ecf5aad1d4ab4ea98ed2f96ad4e47006dc',
// 'b85479b26bc8fbada4737e90ab2133204f2fa2a9ea33c1e0de4452cbf8fa3be4',
// 'c72e18ea0f9aa5457396e3bf810e9de8df0177c8e4e5bf83a85f871512d645a9'
// ]
// }
Get a Drip from the Metal Faucet
We can get a "drip" of METAL from the Tahoe faucet. Paste the address into the Tahoe faucet website. These METAL are for the Tahoe Testnet and have no monetary value.

The faucet will send some METAL to the address and return a transaction ID (txID). This txID can be used with the Tahoe Testnet Explorer to learn more about the transaction.
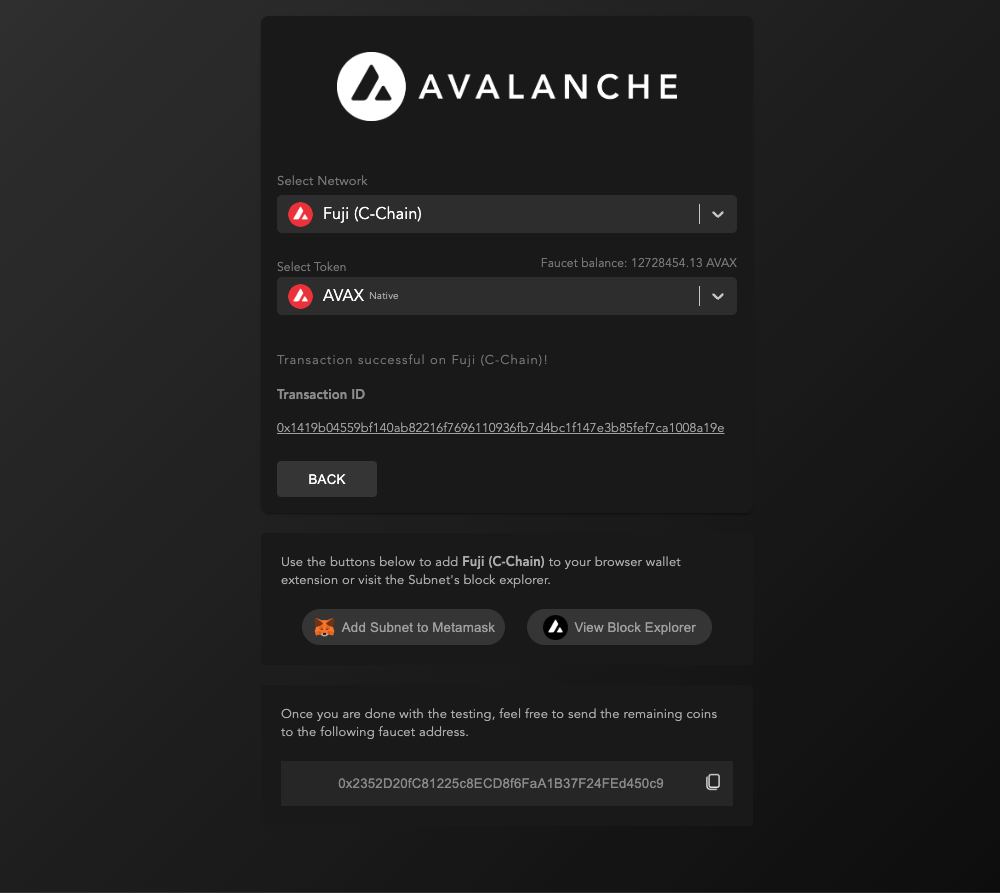
Check the Transaction Details
The txID, 0x1419b04559bf140ab82216f7696110936fb7d4bc1f147e3b85fef7ca1008a19e,
can be seen on the TAHOE Testnet
Explorer.
Metal also has a Mainnet Explorer.
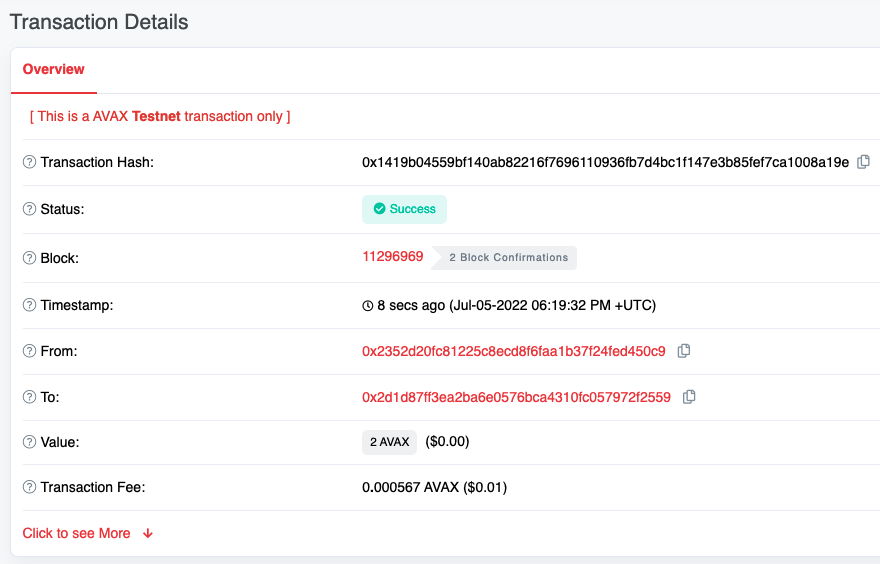
Get the Balance
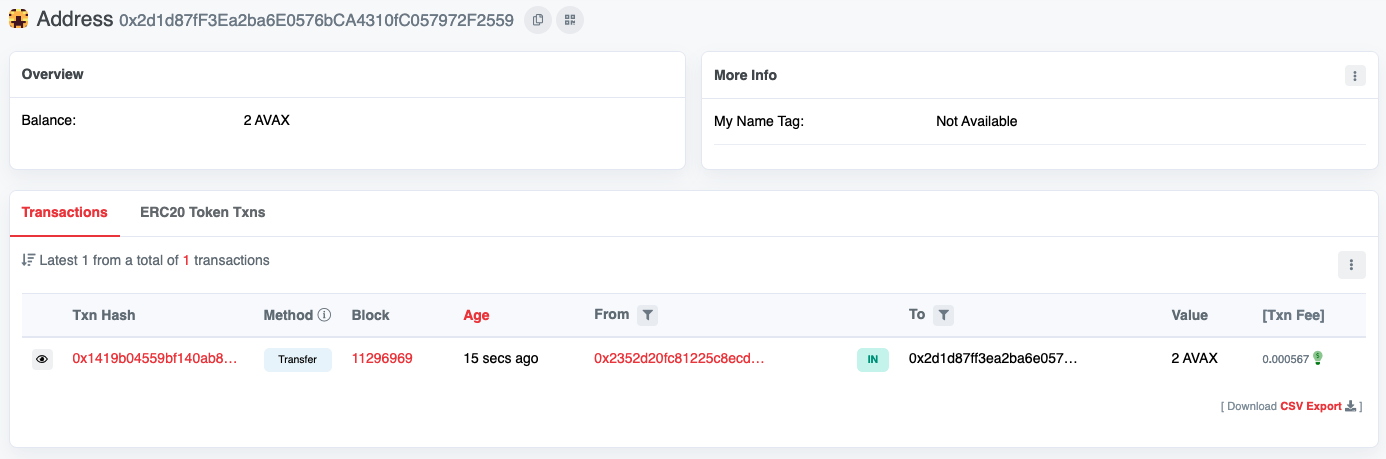
We can also use the Tahoe Explorer to get the balance for the 1st address—0x2d1d87fF3Ea2ba6E0576bCA4310fC057972F2559.
Alternatively, we can use ethersJS to get the balance.
const ethers = require("ethers")
const network = "https://tahoe.metalblockchain.org/ext/bc/C/rpc"
const provider = ethers.getDefaultProvider(network)
const address = "0x2d1d87fF3Ea2ba6E0576bCA4310fC057972F2559"
const main = async (): Promise<any> => {
provider.getBalance(address).then((balance) => {
// convert a currency unit from wei to ether
const balanceInMetal = ethers.utils.formatEther(balance)
console.log(`balance: ${balanceInMetal} METAL`)
// balance: 2 METAL
})
}
main()
Sending METAL
The faucet sent 2 METAL to the first address we generated. Let's send METAL from the 1st address to the 2nd address.
// import ethers.js
import { ethers } from "ethers"
// network: using the Tahoe testnet
const network = "https://tahoe.metalblockchain.org/ext/bc/C/rpc"
// provider: establish and RPC connection to the network
const provider = new ethers.providers.JsonRpcProvider(network)
// Sender private key:
// corresponding address 0x0x2d1d87fF3Ea2ba6E0576bCA4310fC057972F2559
let privateKey =
"cd30aef1af167238c627593537e162ecf5aad1d4ab4ea98ed2f96ad4e47006dc"
// Create a wallet instance
let wallet = new ethers.Wallet(privateKey, provider)
// Receiver Address
let receiverAddress = "0x25d83F090D842c1b4645c1EFA46B15093d4CaC7C"
// AVAX amount to send
let amountInMetal = "0.01"
// Create a transaction object
let tx = {
to: receiverAddress,
// Convert currency unit from ether to wei
value: ethers.utils.parseEther(amountInMetal),
}
// Send a transaction
wallet.sendTransaction(tx).then((txObj) => {
console.log(`"tx, https://tahoe.metaltrace.io/tx/${txObj.hash}`)
// A transaction result can be checked in a Metaltrace with a transaction link which can be obtained here.
})
Verify Success
We can verify that the transaction,
0x3a5f4198b3be8d24b272f8255912aae4dcf2fb1f97f70d1787434de7b3097aac, was
successful using the Tahoe Testnet Explorer. The transaction can be seen
here.
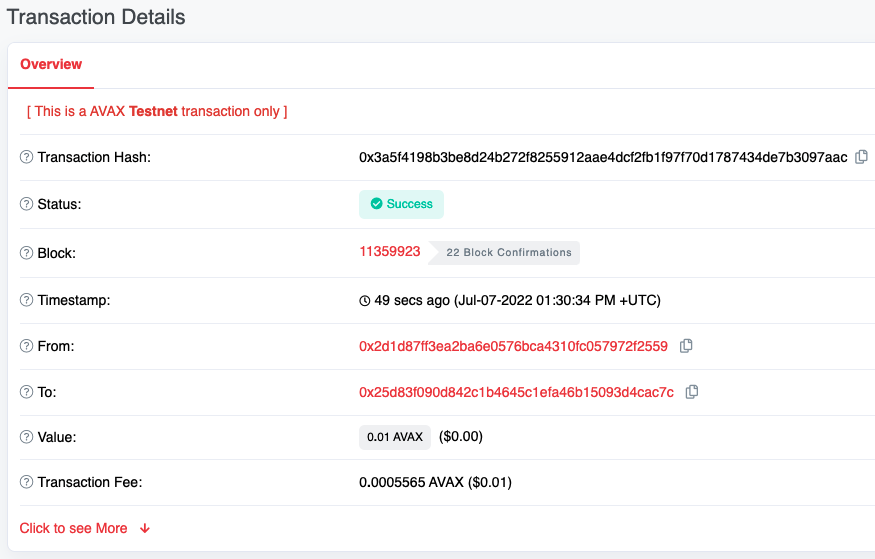
Get the Balance
We can also use the Tahoe Explorer to get the balance for the 2nd address—0x25d83F090D842c1b4645c1EFA46B15093d4CaC7C.
Alternatively, we can use ethersJS to get the balance.
const ethers = require("ethers")
const network = "https://tahoe.metalblockchain.org/ext/bc/C/rpc"
const provider = ethers.getDefaultProvider(network)
const address = "0x25d83F090D842c1b4645c1EFA46B15093d4CaC7C"
const main = async (): Promise<any> => {
provider.getBalance(address).then((balance) => {
// convert a currency unit from wei to ether
const balanceInMetal = ethers.utils.formatEther(balance)
console.log(`balance: ${balanceInMetal} METAL`)
// balance: 0.02 METAL
})
}
main()
Sign Into the Web Wallet
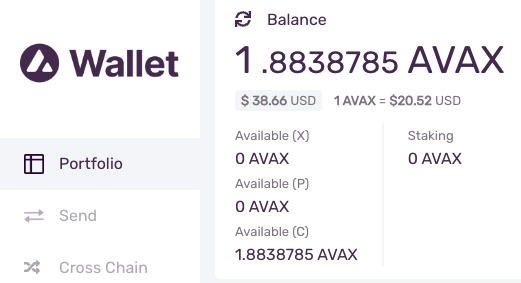
Lastly, we can use the mnemonic to generate a private key to access the Metal Web Wallet. We'll see that it has the METAL balance and that it derives the hexadecimal address from the private key.
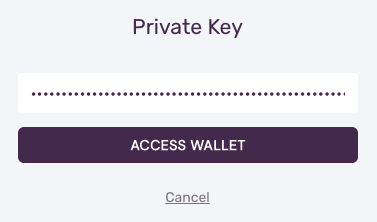
Use the private key to access the Web Wallet.
The balance is correct and the address is the 1st derived address.

We can repeat this login process using the private keys from the remaining 2 addresses in the script above.


Summary
The Tahoe Testnet plays a critical role in testing dapps, smart contracts and financial products before deploying to the Mainnet. Tooling like MetalJS, the public API, faucet, and explorer helps to ensure that your testing and QA environment is close to Mainnet so that you can be confident when you launch on Mainnet.
Resources
For additional and valuable resources please see below.
Faucet
The Tahoe Faucet sends METAL to X-Chain or C-Chain addresses to help you test. (This testnet METAL has no value.)
Wallet
The Metal Web Wallet is a simple, secure, non-custodial wallet for storing Metal Blockchain assets. It supports Mainnet, Tahoe and custom networks.
Explorer
The Metal Explorer allows you to explore the network on Mainnet and Tahoe.
Public API
See here.
MetalJS Examples
There are over 60 example MetalJS scripts which demonstrate how to assets and NFTs, send transactions, add validators and more.